Why Is A Strong Back Important
Exercises for a Strong Back. Although it’s important to strengthen all of your muscles. Strengthening your back is especially vital to your well-being. It’s involved in every pulling, lifting, and carrying action you make. Moreover, it protects your spine from injury!
Here are some of the main benefits of strengthening your back with these bodyweight back exercises:
- Improves spinal stability
- Helps prevent back pain
- Improves posture
- Strengthens you for all the pulling, lifting and carrying movements in life
- Helps maintain a good body composition
Moreover, your back makes up the second largest portion of your musculature (after the legs), so training them expends a lot of energy, allowing you to burn tons of calories.
Benefits of a Stronger Back
Exercises for a Strong Back. The World Health Organisation reports that 60-70 per cent of people. Will experience lower back pain at some point in their lives. One benefit of building strong back muscles is it reduces your risk of developing pain in the back.
For example, a 2016 study involved 36 individuals with chronic back pain. Participants who engaged in strength training exercises twice a week for 12 weeks. Also, had lower pain levels than those in the control group. When they combined these exercises with walking, their pain was reduced even more.
A Healthy Posture
Exercises for a Strong Back. Stronger back muscles also support a healthy posture. When your spine is straight while sitting or standing, your central nervous system can communicate effectively. Your spinal discs and vertebrae don’t impinge on the nerves flowing through them. This enables your brain to send and receive messages with your organs and other systems.
Finally, having strong back muscles makes it easier to do everyday activities. This includes lifting grocery bags, picking up your children or grandchildren, and doing things like lawn work.
1. Wide Grip Kneeling Push up
Target: Lats, Pectoralis major and minor, Shoulder, Arms and Core
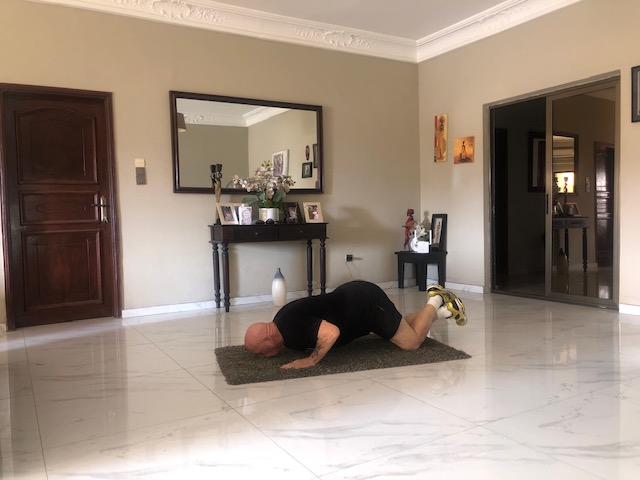

How To Do It
- Start in a standard kneeling push-up position with your ankles crossed and your hands placed slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Keeping your core engaged, lower your body until your chest is just inches from the ground.
- Pause for a moment at the bottom of the movement, then press back up to the starting position.
- Repeat for 10 repetitions.
2. Bird Dog
Target: The main target of the bird dog is the erector spinae muscle. This long back muscle extends the length of the spine from the skull, neck, and ribs to the vertebrae and sacrum of the hip. It is responsible for extending, flexing, and rotating the spine. Also, the rectus abdominis and glutes
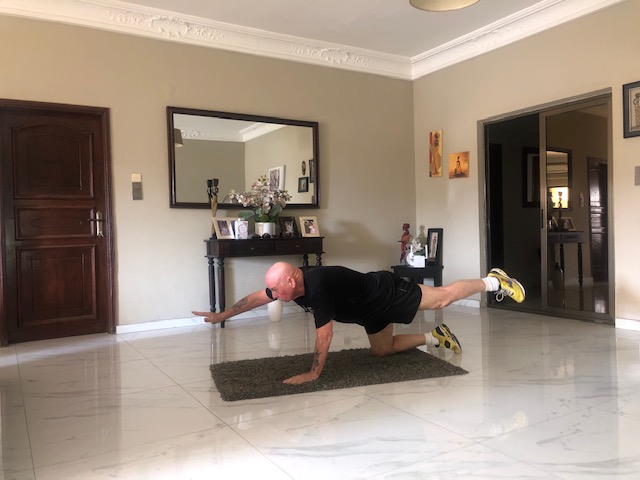

How To Do It
- Get down on your hands and knees with your hands directly below your shoulders and your knees directly below your hips.
- Keeping your back flat and core braced, simultaneously extend your left leg straight behind you and your right arm straight in front of you.
- Pause, and then return to the starting position.
- Repeat with your right leg and left arm.
- Do 10, 5 on each side, or whatever you can manage
3. Reverse Plank
Target: The reverse plank focuses on core strength. We’re talking about abs of steel and a super strong lower back, a part of the body that commonly suffers from everyday activities, even just sitting still!
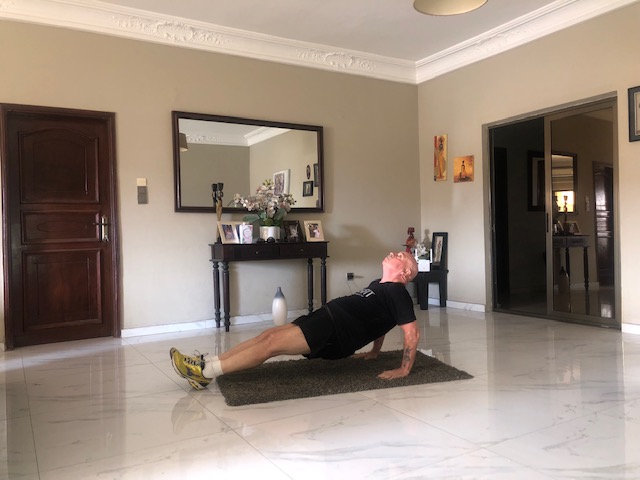

How To Do It
- Step 1. Sit on the floor (or yoga mat if you have one) with your hands firmly on the ground behind you, fingertips facing forward.
- Step 2. Straighten your legs in front of you, heels resting on the ground. You are now in the starting position.
- Step 3. Push your hips and your glutes up from the ground until you have formed a straight line from head to your heels, toes pointed forwards.
- Step 4. Squeeze your abdominals tight – imagine you are squeezing your belly button into your spine and holding the position for as long as you can.
- Step 5. Initially, this may be just a few seconds. The key is to keep a straight line from your head to your heels. Do not allow your hips to drop.
- Step 6. Relax back into the starting position.
- Step 7. Remember, form is vital, so a shorter hold with correct form is far better than a longer hold without. Build up slowly to 30 seconds over time.
4. Modified One Hand Kettlebell Swing
Target: · Improves Balance and Spinal Stability: Kettlebell swings work all of the important balance muscles – glutes, hamstrings, quads, calves, core, hips – and it works all the muscles protecting your spine – erector spinae muscles.
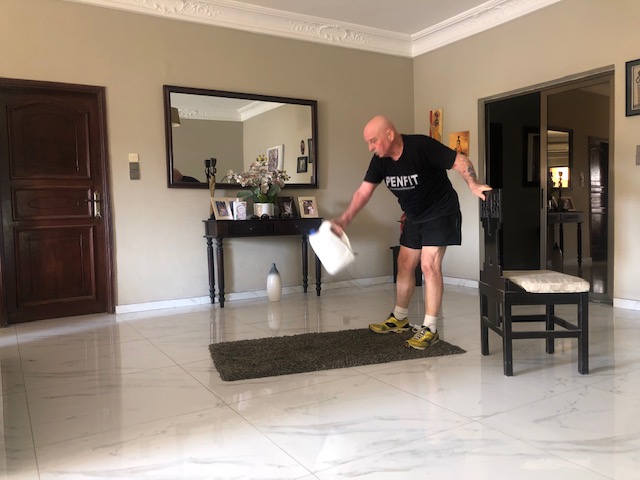

How To Do It
- Stand upright with feet shoulder-width apart with the weight just forward of your feet
- With a chair as a stability support at your side, reach down to grip the weight with one hand.
- From the waist hinge back, as you reach down, do not squat.
- Pull the weight back between your legs
- Straighten your body by forcing the glutes forward, which will propel the weight up in front of you, do not try to lift the weight. your arms are simple ropes that support the weight
- As the weight reaches its highest point in front of you, it will seem to pause before going back down.
- As the weight goes down to the position between your legs, do not squat, you will bend your knees a little.
- Repeat for 10 repetitions on each arm.
Exercises for a Strong Back. Complete these exercises on Monday, Wednesday and Friday for 2 weeks; all 4 exercises are 1 set try to do 2 sets or whatever you can manage.
Video
In Conclusion, Exercises for a Strong Back
Exercises for a Strong Back. The lower back is one of the most important areas of the body that needs to be protected and exercised in order for senior citizens to feel comfortable walking, sitting, and standing. Also, every movement the body makes begins with the spine, so an injury to this area of the body can have devastating consequences for elderly individuals.
The spine and lower back are held stable by numerous tiny muscles that work together to create subtle movements that are required for balance. Furthermore, doing back-strengthening exercises is important for seniors to be able to continue functioning independently in their daily lives.
For example, a good lower back exercise might stretch the muscles at the back of the leg, but the lower back itself should remain stable and engaged. In this way, the lower back is strengthened, and the spinal muscles learn to contract and create stability in response to leg movement.
Important Note *
Remember that everyone is different, and it is ultimately YOUR RESPONSIBILITY to find what your body responds to. So please do your due diligence before trying anything new, including getting Medical Advice to ensure your safety and peace of mind.
Connect with me and leave a comment or two on my social media.