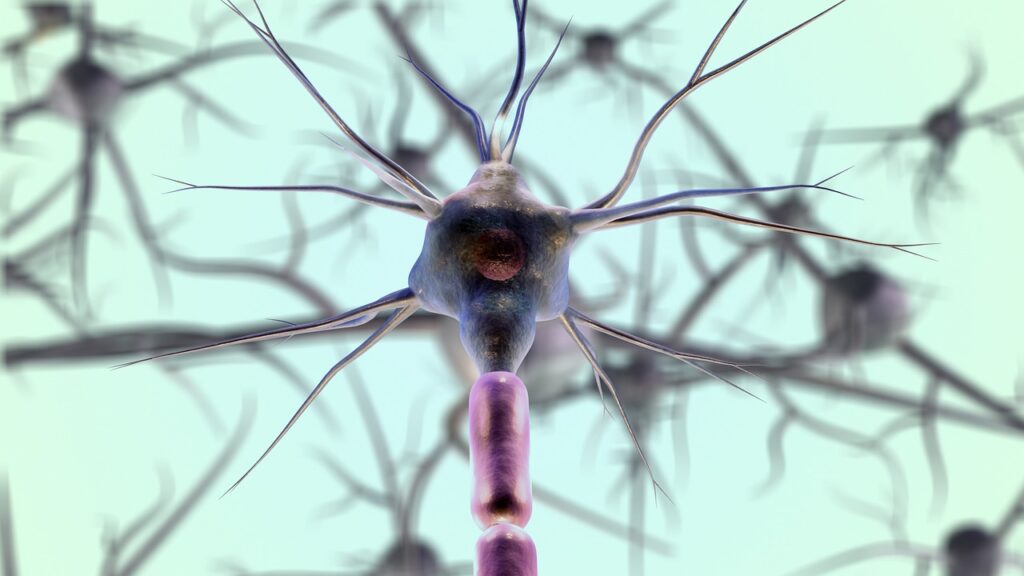
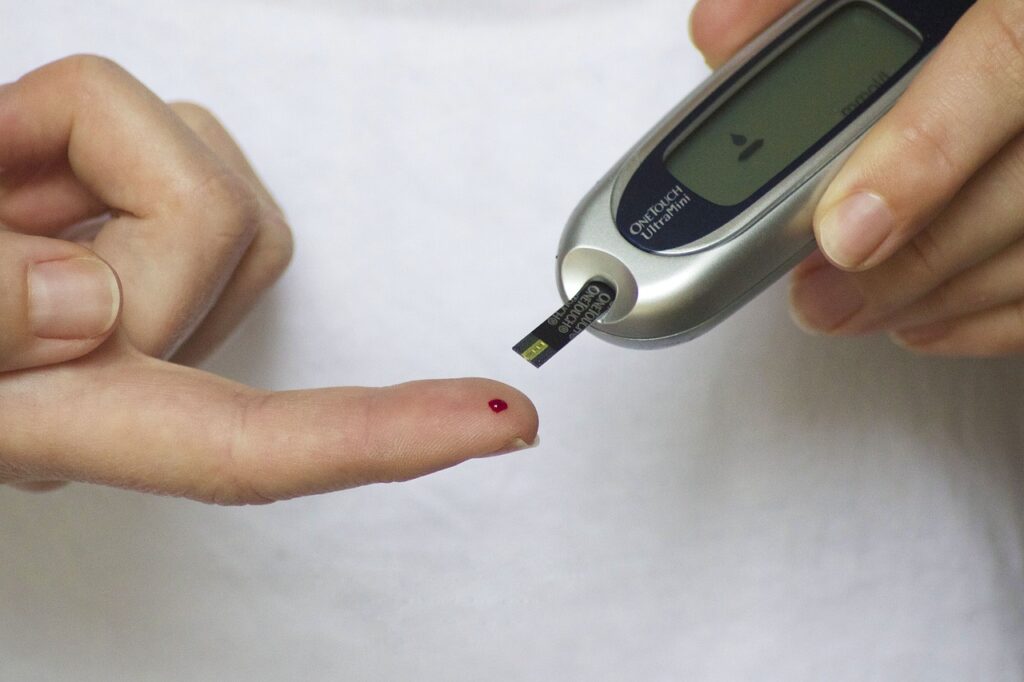
Your Nervous System
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. Your nervous system is your body’s command centre. So then, originating from your brain, it controls your movements, thoughts and automatic responses to the world around you. But it also controls other body systems and processes, such as digestion, breathing and sexual development (puberty). However, diseases, accidents, toxins and the natural ageing process can damage your nervous system.
Serious Statement on Numbness and Tingling
Let’s start with a necessary statement: Here, it’s important to take any signs or symptoms such as numbness and tingling seriously. Also, if you are losing feeling or coordination, having severe muscle weakness, slurred speech, blurred vision, or random muscle movements. Also, any changes in memory or behaviour, don’t wait to contact your healthcare provider. Consequently, these sudden and severe changes should signal you to seek appropriate medical care. So you don’t suffer long-term nervous system damage.
When numbness or tingling is occurring but not to an extreme degree, you may be experiencing peripheral neuropathy. In this case, this condition is a result of peripheral nerve damage. Also, meaning nerves located outside of the brain and spinal cord have been impaired. And this results in pain that can be described as stabbing, tingling, or burning, along with weakness and numbness. In addition, peripheral neuropathy can occur from injuries, infections, certain genes, toxins, and also from autoimmune diseases.
Root Causes
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. So peripheral neuropathy is the cause of numbness and tingling. However, different autoimmune diseases are the root cause of peripheral neuropathy. So then, let’s go into more detail with 7 of these diseases. Additionally, to empower you with the knowledge to positively impact your well-being and autoimmune journey.
What are the parts of the nervous system?
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. The nervous system has two main parts. Each part contains billions of cells called neurons, or nerve cells. These special cells send and receive electrical signals through your body to tell it what to do.
What are the parts of the nervous system?
Central nervous system (CNS):
Your brain and spinal cord make up your CNS. Your brain uses your nerves to send messages to the rest of your body. Each nerve has a protective outer layer called myelin. Myelin insulates the nerve and helps the messages get through.
Peripheral nervous system: (PNS):
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. Your peripheral nervous system consists of many nerves that branch out from your CNS all over your body. This system relays information from your brain and spinal cord to your organs, arms, legs, fingers and toes. Your peripheral nervous system contains your:
- The somatic nervous system, which guides your voluntary movements.
- The autonomic nervous system controls the activities you do without thinking about them
1. Guillain–Barré Syndrome
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. Guillain–Barré syndrome, or GBS, is a rare neurological and autoimmune disorder. And in which the immune system attacks the nerves of the PNS (and, much less commonly, the CNS). The first symptoms typically occur as tingling and weakness in the feet and hands. However, it may not progress to anything more serious. But in some cases, the tingling sensations spread rapidly and eventually paralyze your entire body. Consequently, it requires hospitalization for treatment and recovery.
Guillain–Barré can affect anyone at any age, and the exact cause is unknown. It’s neither contagious nor inherited. However, up to 67% of patients reported having an infection in the 6 weeks leading up to their GBS diagnosis. Infections could come from various sources such as the Zika virus, a respiratory or gastrointestinal infection, or even COVID–19.
Besides tingling, muscle weakness is the chief symptom of GBS. You can reach your weakest state 2 or 3 weeks after initial symptoms appear. And may also experience difficulty with the muscles that control the eyes and mouth. Also, problems with bladder control, and severe pain, particularly at night.
Recovery
Fortunately, recovery is possible even in the most severe cases of GBS through 2 treatments. The first is plasma exchange, where your plasma is extracted from your blood. Because plasma contains antibodies, removing some plasma can reduce the number of antibodies that have been attacking the nerves. The second treatment, high-dose immunoglobulin therapy, provides intravenous injections. Of the proteins created by the immune systems of healthy donors that attack infections. Which can lessen the immune system’s attack on the nervous system.
GBS vs. CIDP
Guillain–Barré is typically considered an acute, short-term disease. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP) is another rare type of autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks myelin sheaths. Myelin is the fatty, protective covering on the nerve fibres. Considered to be a chronic, long-term disease, CIDP is thought to be related to GBS. They share the same set of symptoms, which can make it hard to receive a distinct diagnosis. However, if your symptoms are lasting longer than 8 weeks your doctor may suspect it’s CIDP instead of GBS. It can be treated in much the same way as GBS. Here, you can find more helpful information on both of these diseases from GBS/CIDP Foundation International.
2. Sjögren’s Syndrome
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. Sjögren’s syndrome is described as a systemic autoimmune disorder that affects the eyes, mouth, and other areas when the immune system attacks the glands that make tears and saliva. The classic symptoms are dry mouth, dry eyes, or a combination of both, but the effects can be felt throughout the entire body, including inflammation of the nervous system.
Severe neuropathy and limb weakness are associated with Sjögren’s syndrome, and although there is no known cure. Immunosuppressive therapy can be effective in treating the immune reaction. Sjögren’s Foundation shares reliable health information on this condition. And is working to reduce the time it takes to receive a proper diagnosis.
3. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. This autoimmune disorder, commonly referred to as SLE or lupus, constitutes chronic inflammation of connective tissues, which can affect any organ system and even the nervous system itself. Nerve damage from SLE can cause changes in sensation throughout the body, such as fingers or toes becoming numb when exposed to cold or stress. Lupus has many ways of manifesting in the body and is different for each individual living with this condition. The Lupus Foundation of America is a useful resource if you want to further your knowledge of the disease.
4. Type 1 Diabetes
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. In type 1 diabetes. The immune system is thought to have a reaction that destroys the insulin-making cells in the pancreas. This process can be drawn out for months or years before symptoms become noticeable. If you have type 1 diabetes, you may have decreased sensation in the feet and legs due to diabetic neuropathy. Including a host of other symptoms caused by blood sugar imbalance.
More than half of all people with diabetes (including type 2) will develop some type of neuropathy. That affects feeling in the limbs, making diabetes one of the most common causes of peripheral neuropathy.
5. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Causes of Numbness and Tingling. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that occurs when your immune system attacks the cells lining your joints. Which makes the joints inflamed, stiff, and painful. The cause is unknown and there is no cure (yet!). But early diagnosis and treatment can prevent flare-ups for months or years at a time.
A possible and common complication of RA is carpal tunnel syndrome. When nerves that control the movement and sensation in the hands are compressed. You may have numbness and aching throughout the hands and wrists, or tingling in the fingers and thumbs. Keeping inflammation under control is key to managing RA successfully in the long term. And reduces the risk of having debilitating complications like carpal tunnel syndrome. Do you want more RA information? Find out about it here, that describes RA treatments and how RA differs from osteoarthritis.
6. Multiple Sclerosis
Numbness and tingling may be the very first symptoms you experience at the onset of multiple sclerosis (MS). These abnormal sensations may be felt in the arms, legs, or torso. They are typically spread out over the course of a few days. The immune system attacks the myelin sheaths of the CNS, damaging or scarring the sheaths and potentially the nerves underneath. Multiple sclerosis can get progressively worse over time or may come and go with relapses and remissions. It differs from CIDP because, in MS, the CNS myelin sheaths are attacked. Whereas in CIDP the PNS myelin sheaths are attacked. The National Multiple Sclerosis Society is a useful resource to dig deeper into this condition.
7. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
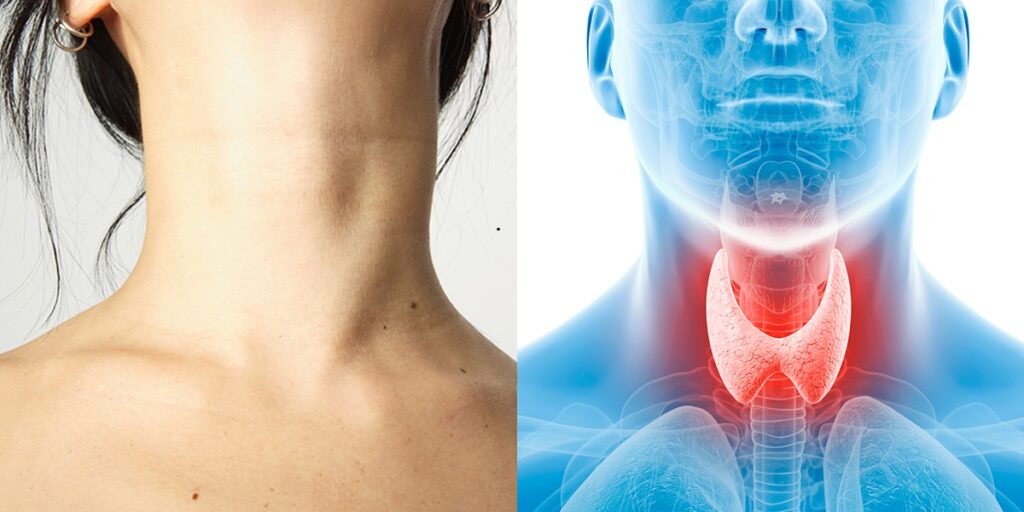
A Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, or Hashimoto’s disease, is an autoimmune condition in which thyroid cells are attacked by the immune system. And the thyroid gland is gradually destroyed. Hashimoto’s disease is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in the United States.
When severe hypothyroidism is left untreated, it can cause peripheral neuropathy. Hypothyroidism can cause fluid retention, and when tissues are swollen, additional pressure is put on peripheral nerves causing numbness, and tingling. Also potentially carpal tunnel syndrome as well. Although it can take years for Hashimoto’s disease to develop and present symptoms, tingling and numbness are just 2 of the many possible physical and mental symptoms associated with Hashimoto’s.
Pensioner Fitness Awards
THE BUSINESS CONCEPT, BEST IN BUSINESS AWARDS 2023
MOST INSPIRING SENIOR WELLNESS WEBSITE 2023
THE GLOBAL HEALTH AND PHARMA, FITNESS AND NUTRITION AWARDS 2023
BEST SENIOR FITNESS AND NUTRITION SPECIALIST 2023
In Conclusion
There are multiple autoimmune diseases that can cause the symptoms known as peripheral neuropathy. Some conditions can progress rapidly and cause extensive damage if medical intervention is not received early on. Different treatments to suppress the immune response are helpful to allow the body a chance to heal, but it’s important to approach healing from a holistic perspective and consider lifestyle factors that can be changed to promote healthy behaviours.
The 7 autoimmune diseases we’ve discussed are not exhaustive of all the conditions that may cause numbness and tingling. It’s vital to discuss all your symptoms with your care team and present a thorough health history to determine what the root cause underlying your symptoms might be. If you’re in need of support and aren’t sure where to begin on your autoimmune journey, take WellTheory’s 2–minute questionnaire to get some direction for your path to healing.
Numbness and tingling are symptoms that should be taken seriously. Advocate for yourself and your unique symptoms to enable your care team to discover the right diagnosis and set you on a successful path toward healing — because your well-being is worth it.
Important Note *
Remember that everyone is different, it is ultimately YOUR RESPONSIBILITY to find what your body responds to. So please do your due diligence before trying anything new, including getting Medical Advice to ensure your safety and peace of mind.
Connect with me and leave a comment or two on my social media.